Contents
close all;
PHANTOM
pha=uff.phantom();
pha.sound_speed=1540;
pha.points=[0, 0, 40e-3, 1];
fig_handle=pha.plot();
PROBE
prb=uff.linear_array();
prb.N=128;
prb.pitch=300e-6;
prb.element_width=270e-6;
prb.element_height=5000e-6;
prb.plot(fig_handle);
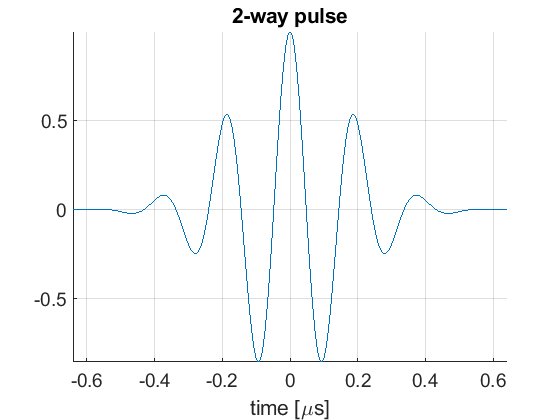
PULSE
pul=uff.pulse();
pul.center_frequency=5.2e6;
pul.fractional_bandwidth=0.6;
pul.plot([],'2-way pulse');
SEQUENCE GENERATION
N=128;
seq=uff.wave();
for n=1:N
seq(n)=uff.wave();
seq(n).probe=prb;
seq(n).source.xyz=[prb.x(n) prb.y(n) prb.z(n)];
seq(n).apodization=uff.apodization();
seq(n).apodization.window=uff.window.sta;
seq(n).apodization.origin=seq(n).source;
seq(n).sound_speed=pha.sound_speed;
fig_handle=seq(n).source.plot(fig_handle);
end
SIMULATOR
sim=fresnel();
sim.phantom=pha;
sim.pulse=pul;
sim.probe=prb;
sim.sequence=seq;
sim.sampling_frequency=41.6e6;
channel_data=sim.go();
USTB's Fresnel impulse response simulator (v1.0.7)
---------------------------------------------------------------
SCAN
scan=uff.linear_scan('x_axis',linspace(-2e-3,2e-3,200).', 'z_axis',linspace(39e-3,41e-3,100).');
scan.plot(fig_handle,'Scenario');
PIPELINE
pipe=pipeline();
pipe.channel_data=channel_data;
pipe.scan=scan;
pipe.transmit_apodization.window=uff.window.tukey50;
pipe.transmit_apodization.f_number=1.7;
pipe.receive_apodization.window=uff.window.tukey50;
pipe.receive_apodization.f_number=1.7;
pre = preprocess.demodulation();
mid = midprocess.das();
mid.dimension = dimension.receive();
b_data=pipe.go({pre mid});
Estimating power spectrum
Band-pass filtering
Low-pass filtering
USTB General beamformer MEX v1.1.2 .............done!
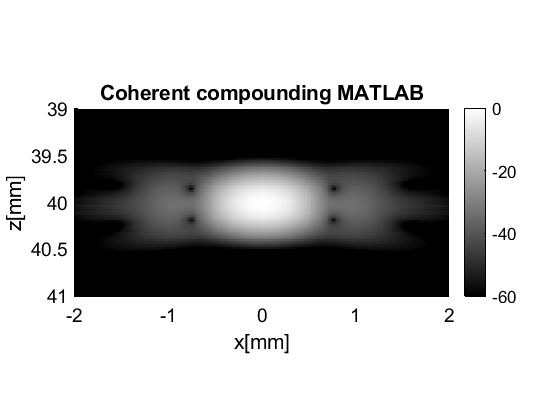
coherently compounded
cc=postprocess.coherent_compounding();
cc.input=b_data;
cc_data=cc.go();
cc_data.plot([],cc.name);

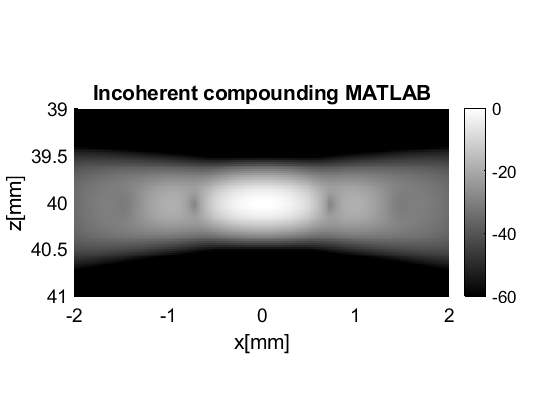
incoherently compounded
ic=postprocess.incoherent_compounding();
ic.input=b_data;
ic_data=ic.go();
ic_data.plot([],ic.name);
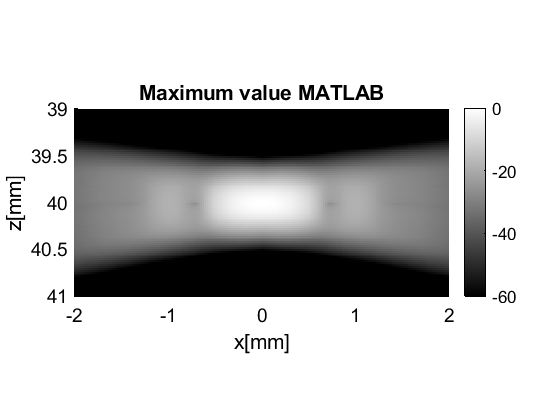
max
mv=postprocess.max();
mv.input=b_data;
mv_data=mv.go();
mv_data.plot([],mv.name);
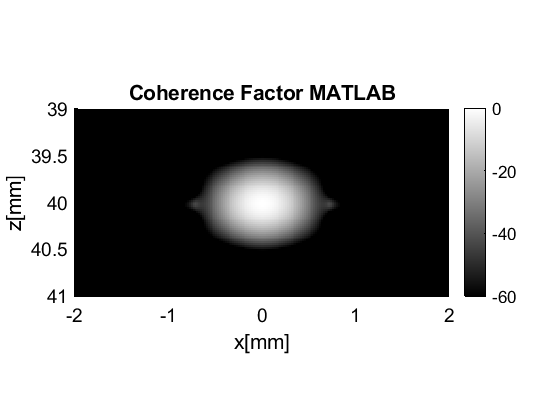
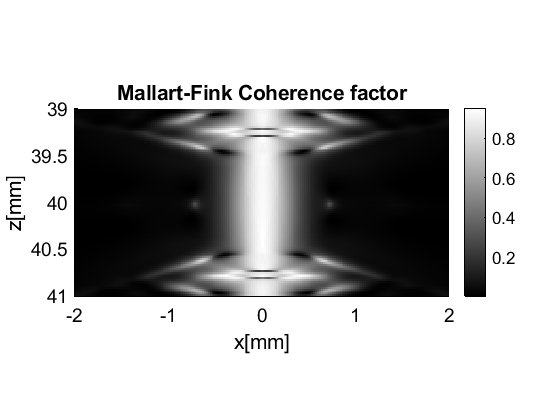
Mallart-Fink coherence factor
cf=postprocess.coherence_factor();
cf.transmit_apodization=pipe.transmit_apodization;
cf.receive_apodization=pipe.receive_apodization;
cf.dimension = dimension.transmit;
cf.input=b_data;
cf_data=cf.go();
cf.CF.plot([],'Mallart-Fink Coherence factor',60,'none');
cf_data.plot([],cf.name);
uff.apodization: Inputs and outputs are unchanged. Skipping process.

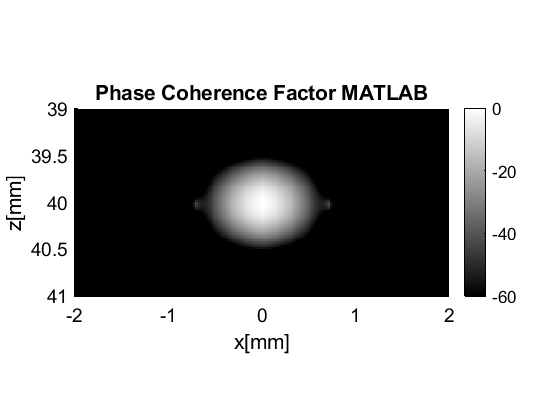
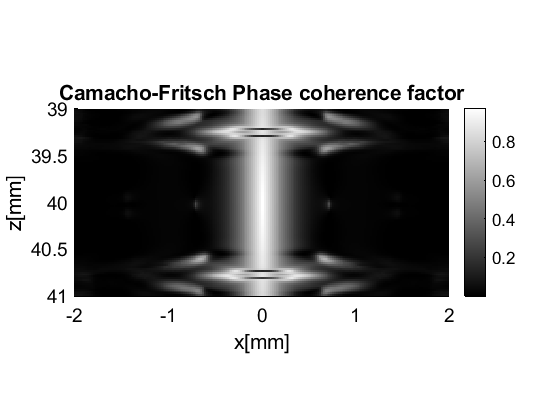
Camacho-Fritsch phase coherence factor
pcf=postprocess.phase_coherence_factor();
pcf.dimension = dimension.transmit;
pcf.transmit_apodization=pipe.transmit_apodization;
pcf.receive_apodization=pipe.receive_apodization;
pcf.input=b_data;
pcf_data=pcf.go();
pcf.FCC.plot([],'Camacho-Fritsch Phase coherence factor',60,'none');
pcf_data.plot([],pcf.name);
uff.apodization: Inputs and outputs are unchanged. Skipping process.