DW simulation with a linear array using the USTB built-in Fresnel simulator
In this example, we show how to use the built-in Fresnel simulator in USTB to generate a Diverging Wave (DW) dataset on a linear array, and then beamform it with USTB.
This tutorial assumes familiarity with the contents of the 'CPWC simulation with the USTB built-in Fresnel simulator' tutorial. Please feel free to refer back to that for more details.
by Alfonso Rodriguez-Molares alfonso.r.molares@ntnu.no and Arun Asokan Nair anair8@jhu.edu 23.02.2017
Contents
Phantom
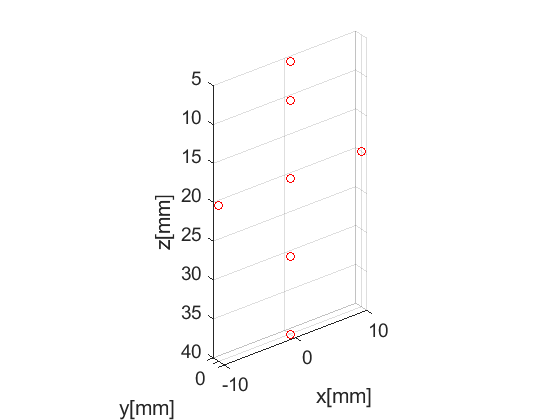
First step - define our phantom. Here, our phantom is a single point scatterer. USTB's implementation of phantom comes with a plot method for free!
pha=uff.phantom(); pha.sound_speed=1540; % speed of sound [m/s] pha.points=[0, 0, 5e-3, 1;... 0, 0, 10e-3, 1;... 0, 0, 20e-3, 1;... 0, 0, 30e-3, 1;... 0, 0, 40e-3, 1;... 10e-3, 0, 20e-3, 1;... -10e-3, 0, 20e-3, 1]; % point scatterer position [m] fig_handle=pha.plot();
Probe
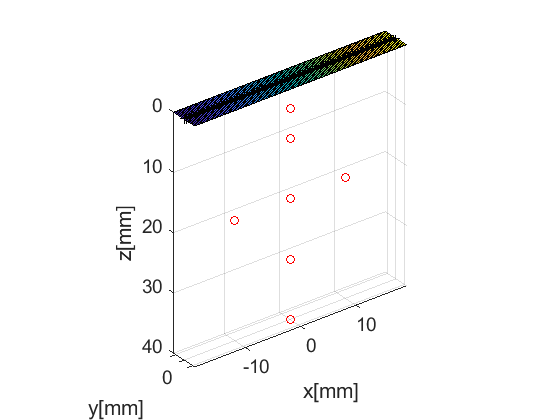
The next step is to define the probe structure which contains information about the probe's geometry. This too comes with a plot method that enables visualization of the probe with respect to the phantom. The probe we will use in our example is a linear array transducer with 128 elements.
prb=uff.linear_array(); prb.N=128; % number of elements prb.pitch=300e-6; % probe pitch in azimuth [m] prb.element_width=270e-6; % element width [m] prb.element_height=5000e-6; % element height [m] prb.plot(fig_handle);
Pulse
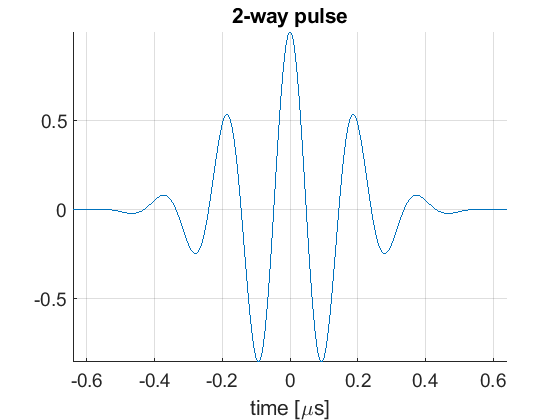
We then define the pulse-echo signal which is done here using the fresnel simulator's pulse structure. We could also use 'Field II' for a more accurate model.
pul=uff.pulse(); pul.center_frequency=5.2e6; % transducer frequency [MHz] pul.fractional_bandwidth=0.6; % fractional bandwidth [unitless] pul.plot([],'2-way pulse');
Sequence generation
Now, we shall generate our sequence! Keep in mind that the fresnel simulator takes the same sequence definition as the USTB beamformer. In UFF and USTB a sequence is defined as a collection of wave structures.
For our example here, we define a sequence of 31 diverging waves. The wave structure has a plot method which plots the direction of the transmitted waves.
N=31; % number of diverging waves x0=linspace(-19.2e-3,19.2e-3,N); z0=-20e-3; seq=uff.wave(); for n=1:N seq(n)=uff.wave(); seq(n).probe=prb; seq(n).source.xyz=[x0(n) 0 z0]; seq(n).sound_speed=pha.sound_speed; % show source fig_handle=seq(n).source.plot(fig_handle); end
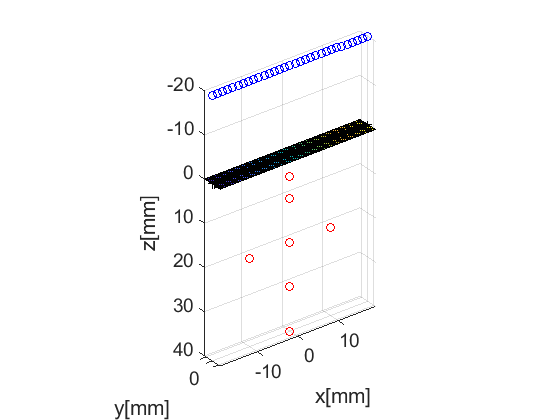
The Fresnel simulator
Finally, we launch the built-in simulator. The simulator takes in a phantom, pulse, probe and a sequence of wave structures along with the desired sampling frequency, and returns a channel_data UFF structure.
sim=fresnel(); % setting input data sim.phantom=pha; % phantom sim.pulse=pul; % transmitted pulse sim.probe=prb; % probe sim.sequence=seq; % beam sequence sim.sampling_frequency=41.6e6; % sampling frequency [Hz] % we launch the simulation channel_data=sim.go();
USTB's Fresnel impulse response simulator (v1.0.7) ---------------------------------------------------------------
Scan
The scan area is defines as a collection of pixels spanning our region of interest. For our example here, we use the linear_scan structure, which is defined with two axes - the lateral axis and the depth axis. scan too has a useful plot method it can call.
scan=uff.linear_scan('x_axis', linspace(-19.2e-3,19.2e-3,200).', 'z_axis', linspace(0e-3,45e-3,100).'); scan.plot(fig_handle,'Scenario'); % show mesh
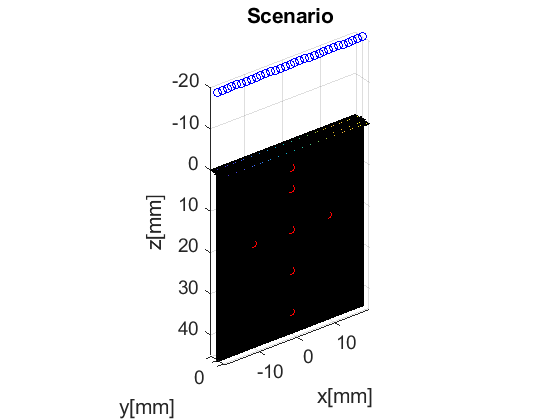
Midprocessor
With channel_data and a scan we have all we need to produce an ultrasound image. We now use a USTB structure pipeline, that takes an apodization structure in addition to the channel_data and scan.
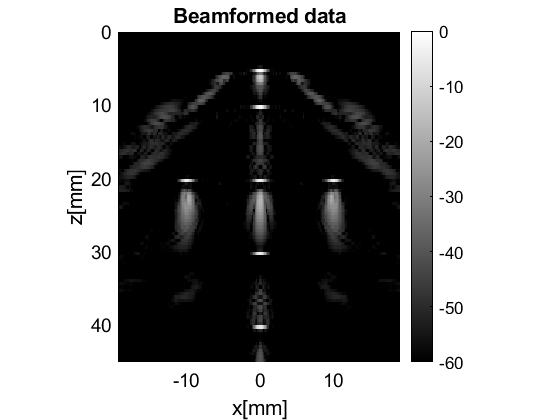
mid=midprocess.das(); mid.dimension = dimension.both; mid.channel_data=channel_data; mid.scan=scan; F_number=1.7; mid.receive_apodization.window=uff.window.hanning; mid.receive_apodization.f_number=F_number; mid.receive_apodization.minimum_aperture = [3e-3 3e-3]; mid.transmit_apodization.window=uff.window.hanning; mid.transmit_apodization.f_number=F_number; mid.transmit_apodization.minimum_aperture = [3e-3 3e-3]; b_data=mid.go(); b_data.plot();
USTB General beamformer MEX v1.1.2 .............done!