Contrast of Delay Multiply And Sum on FI data from an UFF file
by Ole Marius Hoel Rindal olemarius@olemarius.net 28.05.2017
Contents
Setting up file path
To read data from a UFF file the first we need is, you guessed it, a UFF file. We check if it is on the current path and download it from the USTB websever.
clear all; close all; % data location url='http://ustb.no/datasets/'; % if not found downloaded from here local_path = [ustb_path(),'/data/']; % location of example data addpath(local_path); % Choose dataset filename='Alpinion_L3-8_FI_hypoechoic.uff'; % check if the file is available in the local path or downloads otherwise tools.download(filename, url, local_path);
Reading channel data from UFF file
uff_file=uff(filename)
channel_data=uff_file.read('/channel_data');
uff_file =
uff with properties:
filename: 'Alpinion_L3-8_FI_hypoechoic.uff'
version: 'v1.0.1'
mode: 'append'
verbose: 1
UFF: reading channel_data [uff.channel_data]
UFF: reading sequence [uff.wave]
Processed 256/256
%Print info about the dataset
channel_data.print_info
Name: FI dataset of hypoechic cyst recorded on an Alpinion scanner with a L3-8 Probe from a CIRC General Purpose Ultrasound Phantom Reference: www.ultrasoundtoolbox.com Author(s): Ole Marius Hoel Rindal <olemarius@olemarius.net> Muyinatu Lediju Bell <mledijubell@jhu.edu> Version: 1.0.2
Define Scan
Define the image coordinates we want to beamform in the scan object. Notice that we need to use quite a lot of samples in the z-direction. This is because the DMAS creates an "artificial" second harmonic signal, so we need high enough sampling frequency in the image to get a second harmonic signal.
z_axis=linspace(34e-3,48e-3,768).'; sca=uff.linear_scan(); idx = 1; for n=1:numel(channel_data.sequence) sca(n)=uff.linear_scan(channel_data.sequence(n).source.x,z_axis); end
Set up delay part of beamforming
setting up and running the delay part of the beamforming
bmf=beamformer();
bmf.channel_data=channel_data;
bmf.scan=sca;
bmf.receive_apodization.window=uff.window.boxcar;
bmf.receive_apodization.f_number=1.7;
bmf.receive_apodization.apex.distance=Inf;
bmf.transmit_apodization.window=uff.window.none;
b_data=bmf.go({process.delay_matlab_light process.stack});
Create the DMAS image using the delay_multiply_and_sum process
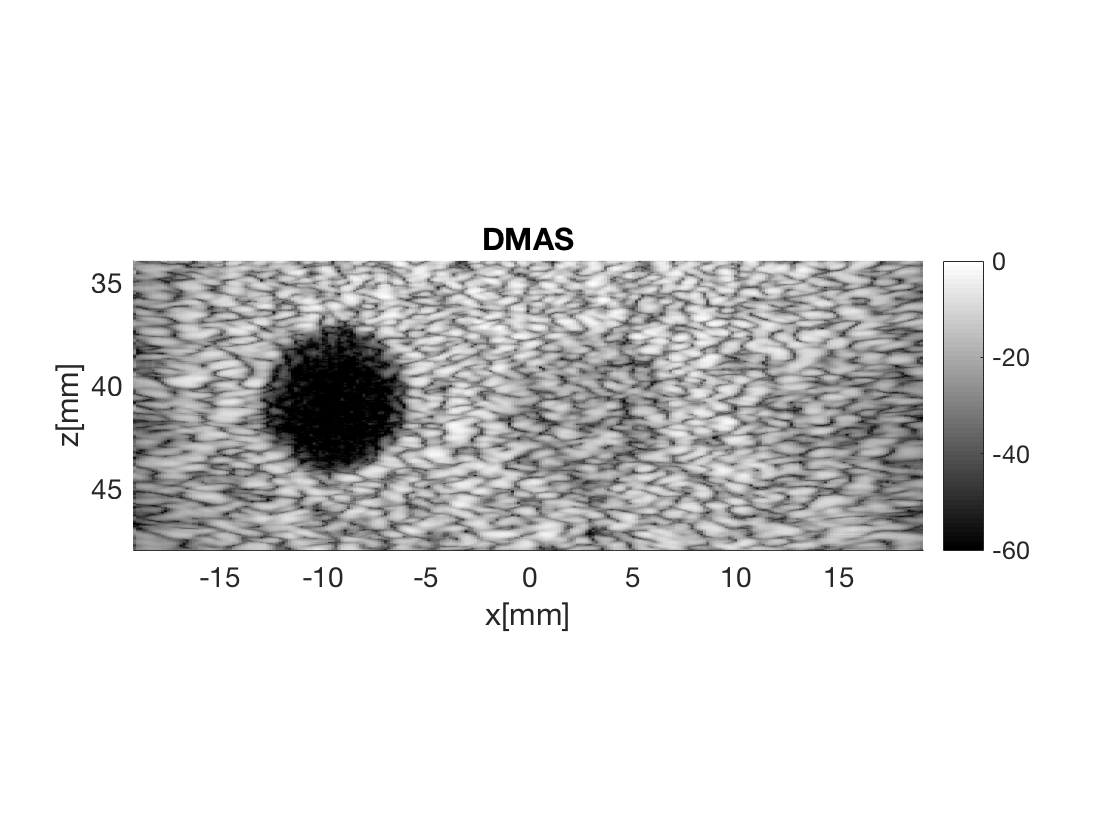
dmas = process.delay_multiply_and_sum(); dmas.dimension = dimension.receive(); dmas.receive_apodization = bmf.receive_apodization; dmas.transmit_apodization = bmf.transmit_apodization; dmas.beamformed_data = b_data; dmas.channel_data = channel_data; dmas.scan = sca b_data_dmas = dmas.go(); % Launch beamformer b_data_dmas.plot(100,'DMAS'); % Display image
dmas =
delay_multiply_and_sum with properties:
dimension: receive
channel_data: [1×1 uff.channel_data]
receive_apodization: [1×1 uff.apodization]
transmit_apodization: [1×1 uff.apodization]
scan: [1×256 uff.linear_scan]
beamformed_data: [1×1 uff.beamformed_data]
name: 'Delay Multiply and Sum'
reference: 'Matrone, G., Savoia, A. S., & Magenes, G. (2015...'
implemented_by: {'Ole Marius Hoel Rindal <olemarius@olemarius.net>'}
version: 'v1.0.2'
Warning: If the result looks funky, you might need to tune the filter paramters
of DMAS. Use the plot to check that everything is OK.
Beamform DAS image
Notice that I redefine the beamformer to use Hamming apodization.
bmf.receive_apodization.window=uff.window.hamming;
bmf.receive_apodization.f_number=1.7;
bmf.receive_apodization.apex.distance=Inf;
bmf.transmit_apodization.window=uff.window.none;
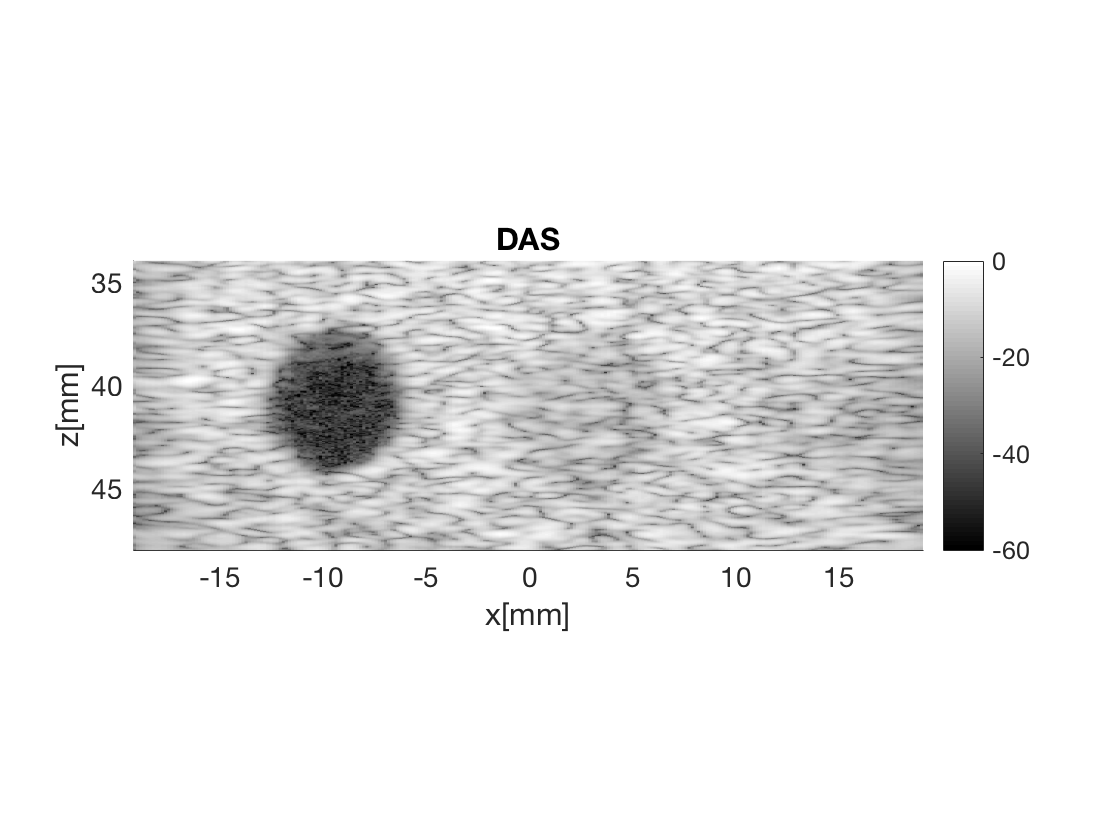
b_data_das=bmf.go({process.das_mex process.stack});
b_data_das.plot(2,'DAS');
Plot both images in same plot
Plot both in same plot with connected axes, try to zoom!
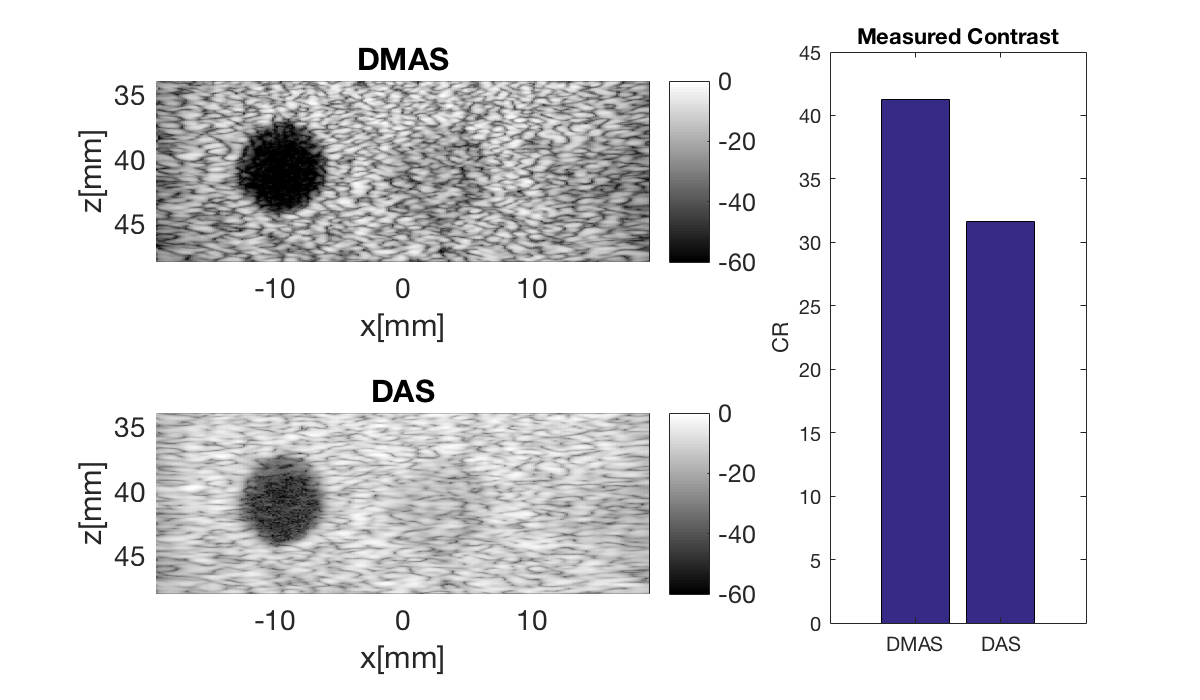
f3 = figure(3);clf set(f3,'Position',[200,200,600,350]) b_data_dmas.plot(subplot(2,3,[1 2]),'DMAS'); % Display image ax(1) = gca; b_data_das.plot(subplot(2,3,[4 5]),'DAS'); % Display image ax(2) = gca; linkaxes(ax);
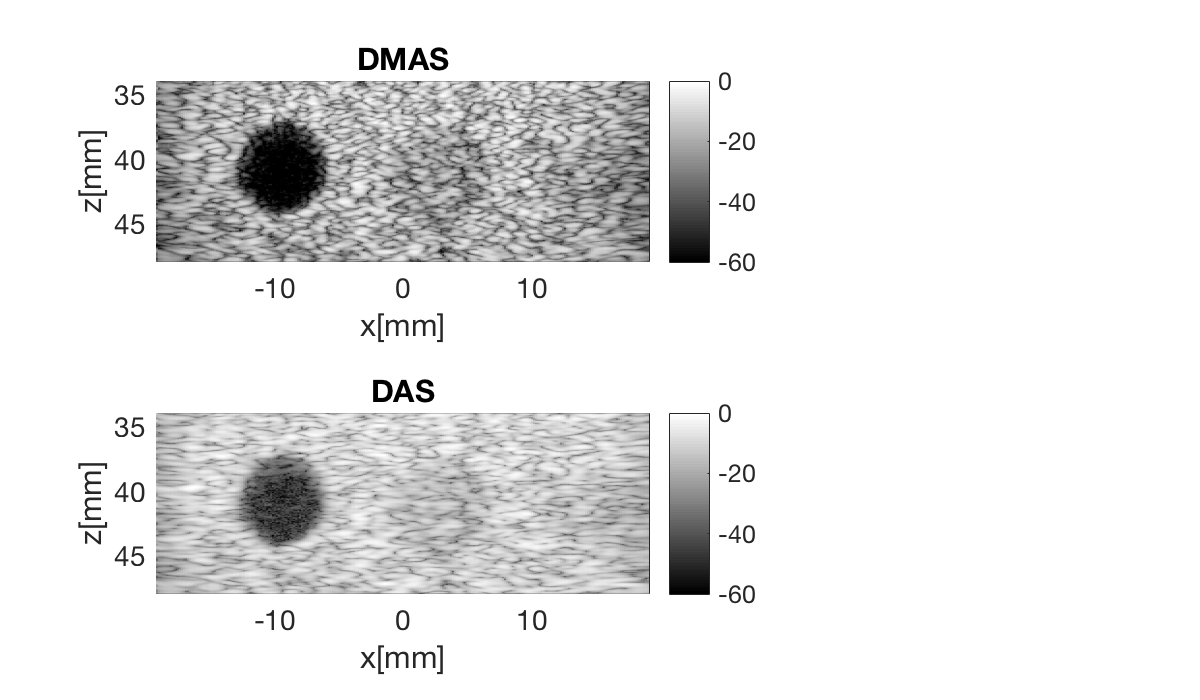
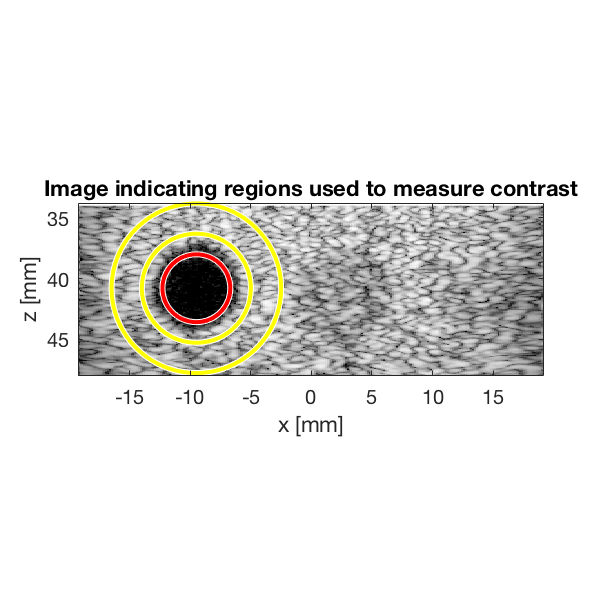
Measure contrast
Lets measure the contrast using the "contrast ratio" as our metric.
% First we need to put our images in a different data struct that the % measure contrast function expects images.all{1} = b_data_dmas.get_image(); images.all{2} = b_data_das.get_image(); % Define the coordinates of the regions used to measure contrast xc_nonecho = -9.5; % Center of cyst in X zc_nonecho = 40.8; % Center of cyst in Z r_nonecho = 2.8; % Radi of the circle in the cyst r_speckle_inner = 4.5; % Radi of the inner circle defining speckle region r_speckle_outer = 7; % Radi of the outer circle defining speckle region % Call the "tool" to measure the contrast [CR] = tools.measure_contrast_ratio(b_data_das,images,xc_nonecho,... zc_nonecho,r_nonecho,r_speckle_inner,r_speckle_outer); % Plot the contrast as a bar graph together with the two images figure(3);hold on subplot(2,3,[3 6]); bar(CR) set(gca,'XTickLabel',{'DMAS','DAS'}) title('Measured Contrast'); ylabel('CR');